On Thursday, Bloomberg NEF published the results of studies on financial investments in green energy, carried out in accordance with the United Nations Environment Research Program and the UNEP Center in Frankfurt. According to published data, investments from 2010 to 2019 in the green energy sector amounted to 2.6 trillion. dollars.
The excitement, due to the ability to generate electricity from new materials, creates an opportunity to reduce greenhouse gas emissions that are harmful to the environment. Reducing the cost of building wind and solar generators, allows projects using advanced technologies to become economically more profitable, compared with power plants using fossil fuels.
“Investments in green energy are investments in a sustainable and reliable tomorrow, which is confirmed by the events of the last decade, with incredibly high growth rates for the construction of environmentally friendly power plants,” said Inger Andersen, Executive Director of UNEP. “In order to achieve real results in preserving the ecology and further increasing the standard of living, we must accelerate the pace of a large-scale transition to green energy.”
Volumetric investments in the “green” energy sector, in fact, make up the increase in funds invested in the electricity industry. According to the IEA (International Energy Agency), until 2025, 322 billion dollars will be invested in renewable sources of green energy (wind, solar and hydroelectric power plants). That is almost three times more than 116 billion that will be invested in the extraction of traditional fuel, and about the same will be invested in electricity networks.
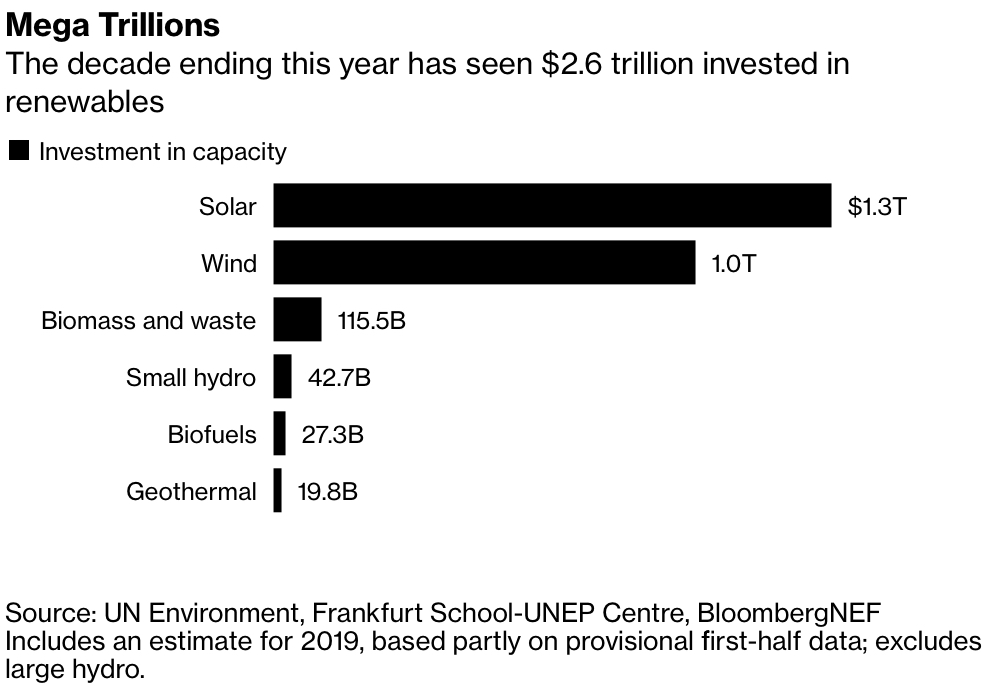
It is clear that the most voluminous investments were made in the construction of new “green” power generators. The total capacity of solar generation over ten years has increased by more than 25 times, from 25 GW from the beginning of 2010 to 663 GW by the end of 2019.
At the same time, at the end of the decade, some problems also appeared. The rate of investment in regenerative energy in 2018 in some large markets decreased compared to previous years. In recent years, the cost of “green” electricity has fallen sharply.
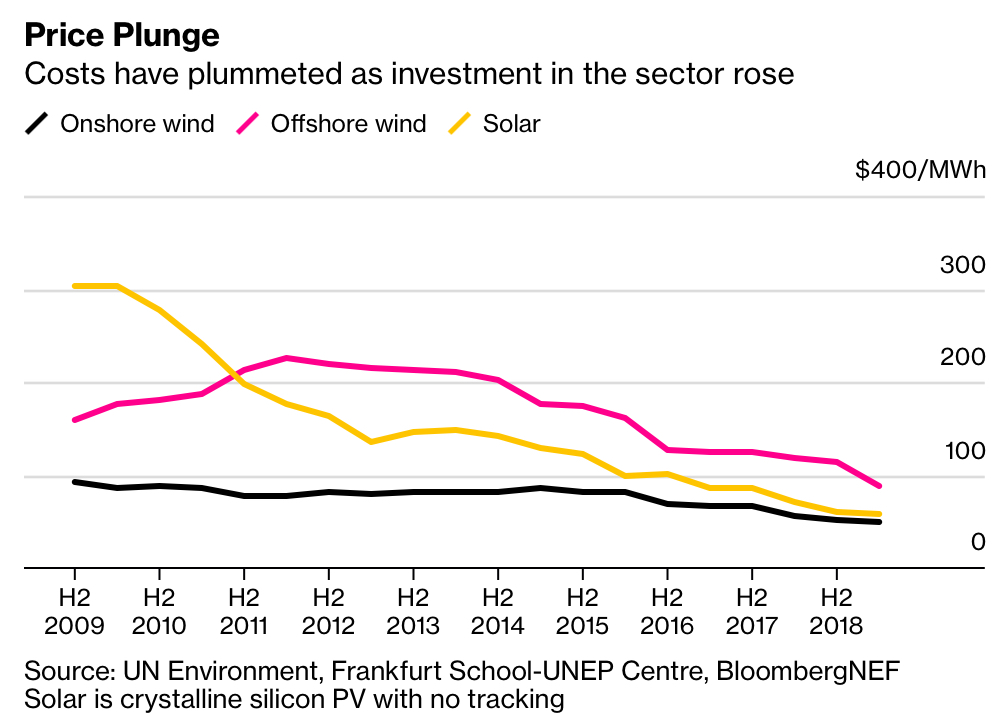
Thus, the construction of new “green” power generators became independent from the state. help. According to research by Bloomberg NEF, the cost of solar cells since 2009 has decreased by 5 times. “The cost of building regenerative generators has changed the choice of the direction of economic development,” said John Moore, BloombergNEF CEO. “In many countries, green energy has become the cheapest form of energy.”
A third of the world’s investment in the construction of regenerative energy sources was made by China. The slowdown in the construction of regenerative generators occurred in 2018, due to the announcement by the government of a decrease in the number of buildings that the state will receive. support.
This reduced investments in regenerative energy in China in the second half of 2018. Investments fell by about 2 times compared to 2017.
Despite large investments in the construction of new regenerative energy sources, they still make up a relatively small share in global electricity production. China, of course, builds the most regenerative plants, but at the same time continues to invest in the construction of new thermal power plants.
According to forecasts, many other regenerative projects will appear in the coming decades. According to Bloomberg NEF, the share of wind and solar energy will increase and by 2050 may reach 48%
. The world increase in electric power amounted to 2.4 TW. Andmost of this increase was obtained from pure sources, but at the same time, a significant part of the increase was obtained from traditional thermal installations.
Europe and the USA sharply reduced production using traditional fuels, but Asia, and especially India, increased the amount of harmful emissions into the atmosphere. As a result, global carbon emissions have increased since the end of 2009 by at least 10%.


